
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce complex and high-precision plastic parts in large volumes. It involves injecting molten plastic into a custom-designed mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the final shape. This method is widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer products due to its efficiency, repeatability, and ability to handle intricate designs.
Injection Molding Capabilities
High Precision Molding
Create complex components with tight tolerances and exact specifications using advanced mold tooling techniques.
Mass Production Efficiency
Produce large volumes of identical parts cost-effectively with consistent quality and speed.
Material Flexibility
Supports a wide range of thermoplastics and elastomers, tailored to your product’s functional and aesthetic needs.
Low Waste Manufacturing
Minimizes scrap and reduces environmental impact through efficient material usage and closed-loop systems.
Fast Cycle Times
Short production cycles enable quicker turnaround and faster time-to-market for your product.
Custom Mold Design
Design and build molds specific to your product's geometry, texture, and performance requirements.
Insert & Over Molding
Combine plastic with metal or other materials to enhance product strength, durability, and functionality.
Prototype to Production
From early-stage prototypes to full-scale manufacturing, we support every phase of product development.
Dimensional Accuracy
Advanced quality control ensures high precision and part uniformity in every production run.
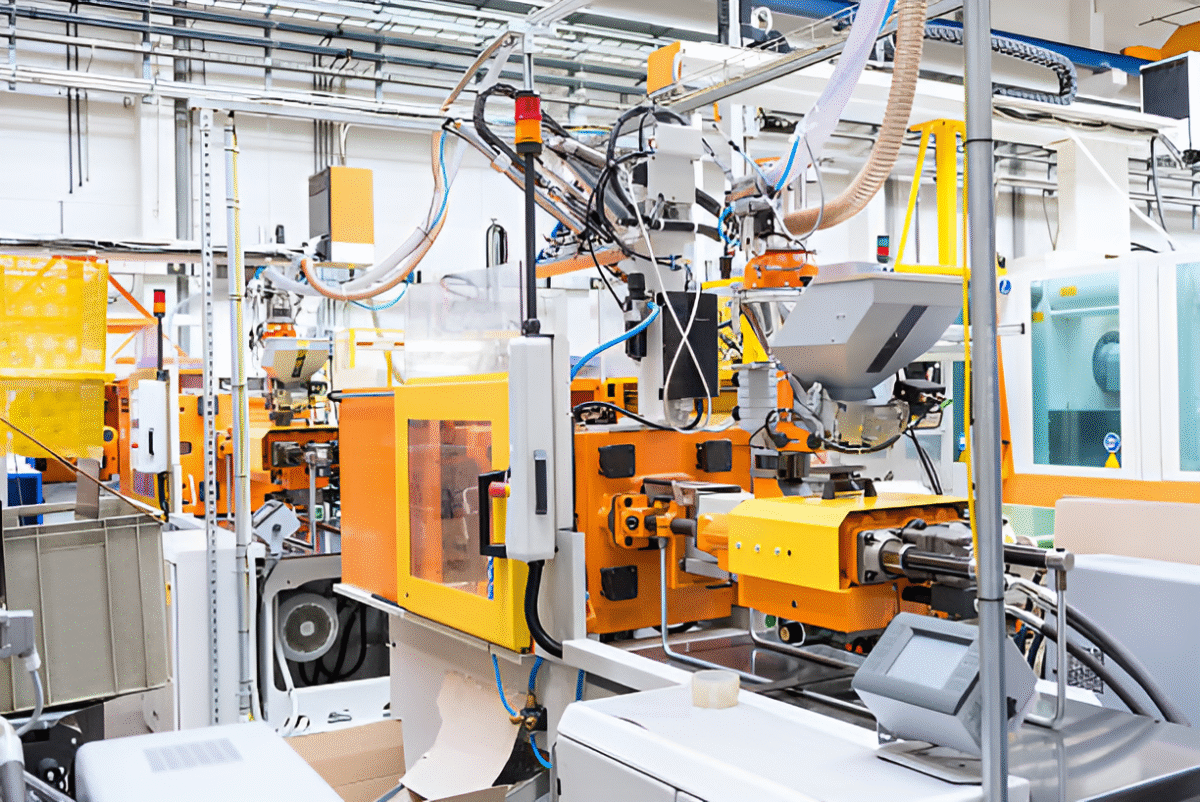
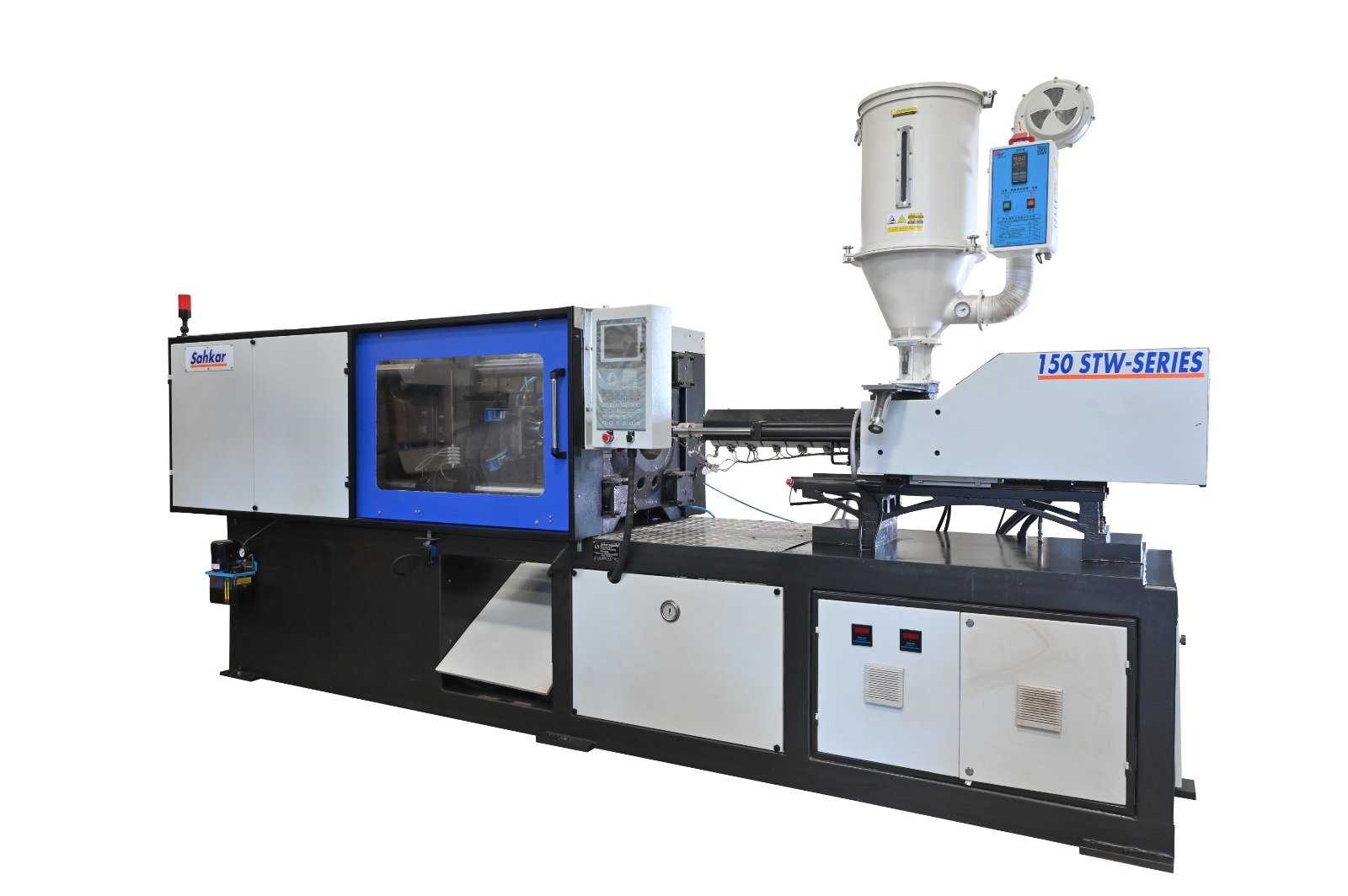
Injection Molding Machines We Have
- FERROMATIK - 110
- TONSL&T - 60
- TONSSTM - 160
- TONSYIZUMI - 120 TONS
Material Versatility
- Compatible with a wide range of thermoplastics and resins.
- Customized material selection for strength, flexibility, or appearance.
- Additives for UV resistance, flame retardance, and color matching.


Production Efficiency
- Fast cycle times reduce lead time and boost productivity.
- Minimal material waste with optimized gating and runners.
- Ideal for cost-effective mass production with low unit cost.
1
Process Identification
Identify repetitive tasks like mold handling, part ejection, and inspection: ideal targets for automation to boost speed and accuracy
2
Data Collection & Analysis
Track cycle times, temperatures, and defect rates. Use this data to uncover inefficiencies and areas where automation can help.
3
Technology Selection
Choose tools like robotic arms for handling, sensors for alignment, vision systems for inspection, and AI for predictive tuning.
4
System Integration
Sync new tech with existing machines using PLCs, SCADA, or IoT systems for real-time coordination and centralized control.
5
Testing & Optimization
Run trials to fine-tune equipment settings, improve data accuracy, and minimize process disruptions for smooth operation.
6
Deployment & Scaling
Expand automation across lines, train operators, and use continuous feedback to enhance efficiency plant-wide
